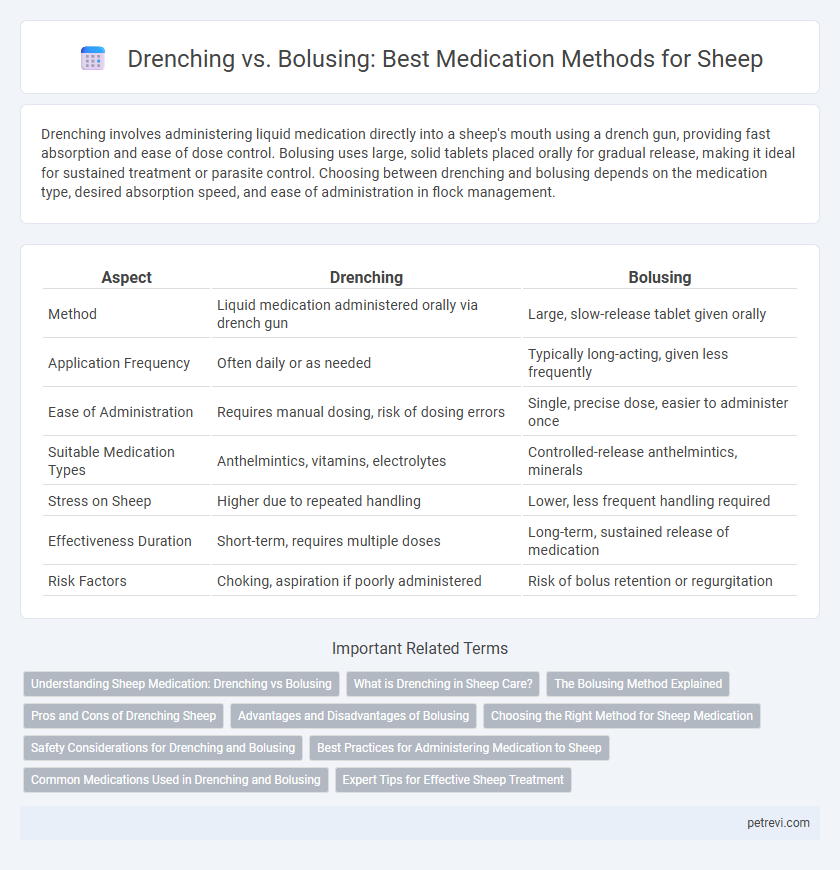
Drenching involves administering liquid medication directly into a sheep's mouth using a drench gun, providing fast absorption and ease of dose control. Bolusing uses large, solid tablets placed orally for gradual release, making it ideal for sustained treatment or parasite control. Choosing between drenching and bolusing depends on the medication type, desired absorption speed, and ease of administration in flock management.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Drenching | Bolusing |
|---|---|---|
| Method | Liquid medication administered orally via drench gun | Large, slow-release tablet given orally |
| Application Frequency | Often daily or as needed | Typically long-acting, given less frequently |
| Ease of Administration | Requires manual dosing, risk of dosing errors | Single, precise dose, easier to administer once |
| Suitable Medication Types | Anthelmintics, vitamins, electrolytes | Controlled-release anthelmintics, minerals |
| Stress on Sheep | Higher due to repeated handling | Lower, less frequent handling required |
| Effectiveness Duration | Short-term, requires multiple doses | Long-term, sustained release of medication |
| Risk Factors | Choking, aspiration if poorly administered | Risk of bolus retention or regurgitation |
Understanding Sheep Medication: Drenching vs Bolusing
Drenching involves administering liquid medication directly into a sheep's mouth using a drenching gun, ensuring rapid absorption and effective treatment of parasites or deficiencies. Bolusing delivers medication in solid form, such as tablets or pellets, designed for slow release and prolonged effect within the rumen, ideal for sustained treatments. Choosing between drenching and bolusing depends on the type of medication, duration of effect needed, and ease of administration for effective flock health management.
What is Drenching in Sheep Care?
Drenching in sheep care involves administering liquid medication orally using a drench gun or syringe to treat internal parasites effectively. It ensures fast absorption of anthelmintics directly into the sheep's digestive system, improving parasite control and overall health. Proper drenching technique is essential to prevent choking and ensure accurate dosage for optimal treatment results.
The Bolusing Method Explained
The bolusing method for sheep medication involves administering a solid, slow-release tablet or pellet directly into the rumen using a bolus gun, ensuring prolonged absorption of the drug. This delivery system maintains effective therapeutic levels over an extended period, making it ideal for sustained treatment of parasitic infections or nutritional supplementation. Proper bolus placement deep in the throat minimizes the risk of injury and ensures optimal medication efficacy.
Pros and Cons of Drenching Sheep
Drenching sheep allows for rapid administration of liquid medication, ensuring precise dosage control and immediate absorption through the gastrointestinal tract. However, it requires careful handling to avoid stress or injury to the animal, and there is a risk of aspiration if performed incorrectly. Compared to bolusing, drenching is less suitable for sustained-release formulations and may necessitate more frequent treatments to maintain therapeutic levels.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Bolusing
Bolusing for sheep medication offers the advantage of providing a controlled, slow-release delivery of medication, ensuring longer-lasting effects and reducing the frequency of treatments. It minimizes the risk of drenching errors, such as dosage inaccuracies or aspiration, improving overall safety and animal welfare. However, bolusing can cause discomfort during administration, requires proper training to avoid injury, and the initial cost of bolus devices may be higher compared to drenching methods.
Choosing the Right Method for Sheep Medication
Choosing the appropriate medication method for sheep depends on factors such as ease of administration, dosage accuracy, and stress reduction. Drenching offers precise dosage control and rapid absorption by delivering liquid medication directly into the rumen, ideal for individual treatments. Bolusing provides a longer-lasting effect through slow-release medications, making it suitable for herd-wide parasite control with less frequent handling.
Safety Considerations for Drenching and Bolusing
Ensuring safety in sheep medication requires careful attention to drenching and bolusing techniques, as improper administration can lead to choking, aspiration pneumonia, or injury. Drenching involves the use of a dosing gun to deliver liquid medication orally, demanding precise handling to avoid causing distress or physical harm to the sheep's throat and esophagus. Bolusing uses solid tablets or pellets, which require correct placement at the back of the tongue to prevent spitting out or inhalation, emphasizing the need for trained personnel to reduce risks and ensure effective treatment.
Best Practices for Administering Medication to Sheep
Drenching and bolusing are two common methods for administering medication to sheep, with drenching involving liquid dosing directly into the mouth and bolusing using a solid tablet or capsule swallowed whole. Best practices for drenching include proper restraint of the sheep, using a drench gun to avoid injury, and administering the correct dosage based on the animal's weight. Bolusing requires careful handling to ensure the sheep swallows the tablet without choking, and verifying the sheep can easily swallow large boluses to prevent stress or aspiration.
Common Medications Used in Drenching and Bolusing
Common medications used in drenching sheep include anthelmintics such as ivermectin, fenbendazole, and levamisole, which target internal parasites efficiently. Bolusing often involves slow-release formulations of minerals and vitamins like copper, cobalt, and selenium to ensure prolonged nutritional supplementation. Both methods are integral for maintaining flock health, with drenching providing immediate parasite control and bolusing supporting long-term nutritional balance.
Expert Tips for Effective Sheep Treatment
Drenching provides rapid medication absorption through the oral cavity, making it ideal for urgent parasite control in sheep, while bolusing delivers a sustained release suitable for long-term nutritional supplementation. Experts recommend precise dosage calculation based on sheep weight and proper restraint techniques to ensure effective administration and minimize stress. Using calibrated equipment and maintaining hygiene during treatment prevents cross-contamination and enhances the overall health outcomes of sheep medical care.
Drenching vs Bolusing for Sheep Medication Infographic
 petrevi.com
petrevi.com