Natural mating in sheep breeding allows for natural genetic diversity and behavioral interactions, promoting herd health and adaptation to local environments. Artificial insemination offers precise genetic selection, disease control, and the ability to introduce superior genetics from distant or rare rams without transporting animals. Farmers often balance these methods to optimize flock improvement, biosecurity, and reproductive efficiency.
Table of Comparison
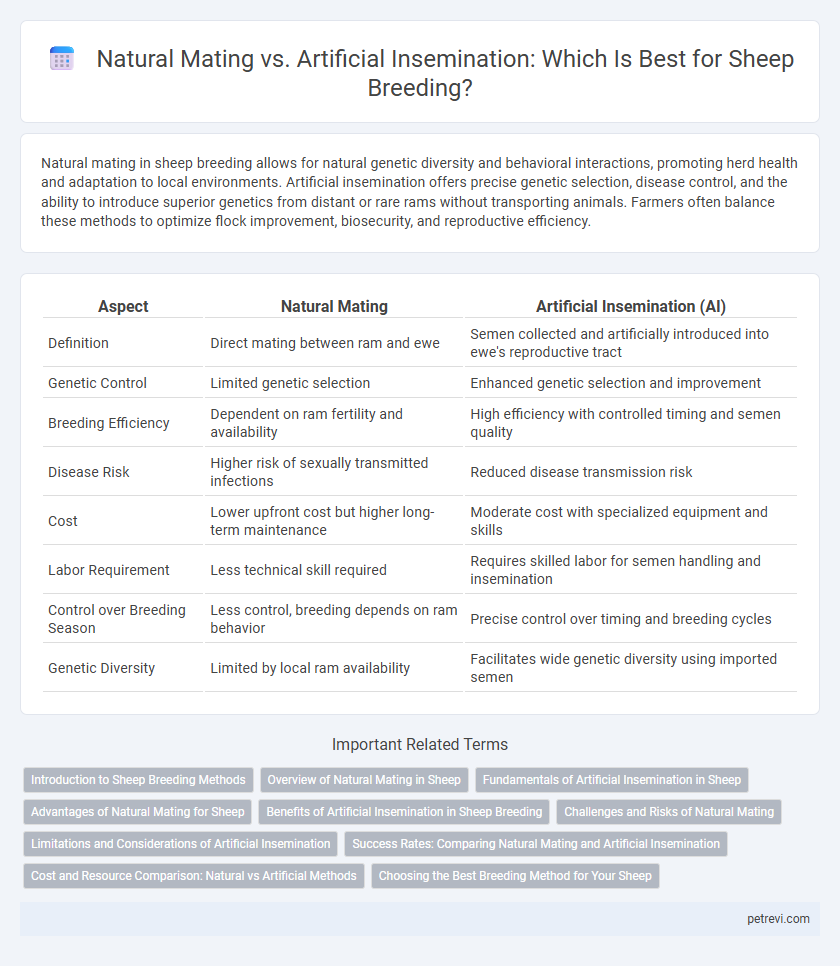
| Aspect | Natural Mating | Artificial Insemination (AI) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Direct mating between ram and ewe | Semen collected and artificially introduced into ewe's reproductive tract |
| Genetic Control | Limited genetic selection | Enhanced genetic selection and improvement |
| Breeding Efficiency | Dependent on ram fertility and availability | High efficiency with controlled timing and semen quality |
| Disease Risk | Higher risk of sexually transmitted infections | Reduced disease transmission risk |
| Cost | Lower upfront cost but higher long-term maintenance | Moderate cost with specialized equipment and skills |
| Labor Requirement | Less technical skill required | Requires skilled labor for semen handling and insemination |
| Control over Breeding Season | Less control, breeding depends on ram behavior | Precise control over timing and breeding cycles |
| Genetic Diversity | Limited by local ram availability | Facilitates wide genetic diversity using imported semen |
Introduction to Sheep Breeding Methods
Natural mating and artificial insemination are two primary sheep breeding methods essential for flock improvement. Natural mating involves direct ram-to-ewe contact, promoting natural selection and behavioral compatibility. Artificial insemination allows precise genetic control and disease prevention by using semen from genetically superior rams without physical mating.
Overview of Natural Mating in Sheep
Natural mating in sheep involves ram and ewe interaction without external intervention, relying on natural behaviors and fertility cycles for reproduction. This method supports genetic diversity and allows rams to exhibit natural mating instincts, benefiting flock social structure. However, it may limit controlled breeding and increase risks of disease transmission compared to artificial insemination.
Fundamentals of Artificial Insemination in Sheep
Artificial insemination (AI) in sheep involves the collection and controlled deposition of semen into the ewe's reproductive tract, enhancing genetic improvement and disease control compared to natural mating. Key fundamentals include semen collection via electroejaculation or artificial vagina, semen evaluation for motility and concentration, and precise timing of insemination aligned with ewe estrus cycles to maximize conception rates. AI techniques, such as cervical or laparoscopic insemination, require skilled handling to overcome anatomical challenges of the sheep cervix, ensuring successful fertilization and herd productivity.
Advantages of Natural Mating for Sheep
Natural mating ensures higher fertility rates in sheep by allowing natural selection and mate compatibility to influence reproduction. It enhances the expression of natural behaviors, which can reduce stress and improve overall flock health. This method also eliminates the need for specialized equipment or technical skills, making it cost-effective for small-scale or remote sheep farmers.
Benefits of Artificial Insemination in Sheep Breeding
Artificial insemination in sheep breeding enhances genetic diversity by enabling the use of superior ram semen from diverse geographic locations without the need for transportation of animals. This method reduces the risk of disease transmission and injury associated with natural mating, promoting healthier flocks and improved animal welfare. Precision in timing and selection during artificial insemination increases lambing rates and allows for controlled breeding schedules, optimizing overall flock productivity.
Challenges and Risks of Natural Mating
Natural mating in sheep breeding poses challenges such as limited genetic diversity and potential transmission of diseases like foot rot or internal parasites. The unpredictability of ram fertility and behavior can lead to inconsistent lambing rates and increased management efforts. Furthermore, physical injuries to ewes during mating and the risk of inbreeding reduce overall flock productivity and health.
Limitations and Considerations of Artificial Insemination
Artificial insemination in sheep breeding faces limitations such as the need for specialized equipment and skilled personnel, which can increase operational costs and complicate farm management. Estrus detection and timing are critical for successful AI, yet sheep's subtle signs and short breeding windows often reduce conception rates compared to natural mating. Moreover, AI may limit genetic diversity if semen from a narrow pool of rams is overused, posing risks to flock resilience and long-term productivity.
Success Rates: Comparing Natural Mating and Artificial Insemination
Natural mating in sheep breeding typically results in a higher conception rate, averaging between 80-90%, due to natural reproductive behaviors and immediate sperm deposition. Artificial insemination (AI) success rates vary widely, often ranging from 50-70%, influenced by factors such as semen quality, timing, and technician skill. Advances in estrus synchronization and semen handling continue to improve AI outcomes, but natural mating remains more reliable under extensive or low-tech farming systems.
Cost and Resource Comparison: Natural vs Artificial Methods
Natural mating in sheep breeding often incurs lower upfront costs as it requires minimal equipment and relies on the shepherd's management of rams and ewes, but it demands more labor and land resources for maintaining breeding flocks. Artificial insemination (AI) involves higher initial expenses for specialized equipment, semen collection, and storage, yet it optimizes genetic diversity and reduces the number of rams needed, lowering maintenance costs over time. Evaluating cost-efficiency depends on flock size, genetic improvement goals, and available resources, with AI providing long-term savings in controlled breeding programs despite higher startup investments.
Choosing the Best Breeding Method for Your Sheep
Natural mating in sheep breeding offers controlled genetic selection through direct ram-ewe interaction, promoting natural behaviors and reducing labor costs. Artificial insemination (AI) enables genetic improvement by accessing superior sires worldwide and increasing reproductive efficiency with precise timing. Selecting the best breeding method depends on flock size, genetic goals, available resources, and management capabilities to optimize lamb production and flock health.
Natural Mating vs Artificial Insemination for Sheep Breeding Infographic
 petrevi.com
petrevi.com