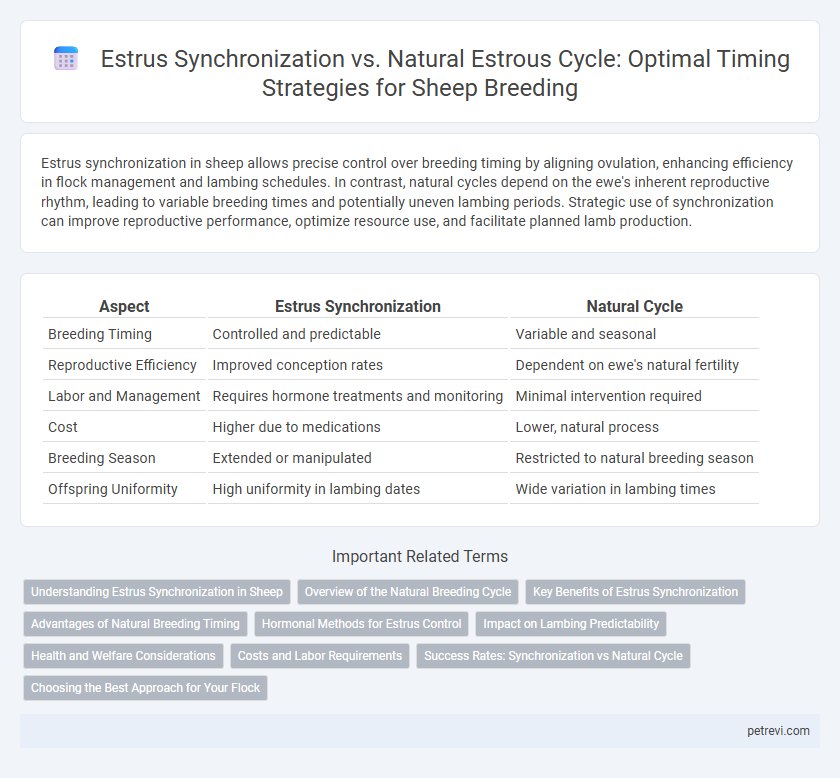
Estrus synchronization in sheep allows precise control over breeding timing by aligning ovulation, enhancing efficiency in flock management and lambing schedules. In contrast, natural cycles depend on the ewe's inherent reproductive rhythm, leading to variable breeding times and potentially uneven lambing periods. Strategic use of synchronization can improve reproductive performance, optimize resource use, and facilitate planned lamb production.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Estrus Synchronization | Natural Cycle |
|---|---|---|
| Breeding Timing | Controlled and predictable | Variable and seasonal |
| Reproductive Efficiency | Improved conception rates | Dependent on ewe's natural fertility |
| Labor and Management | Requires hormone treatments and monitoring | Minimal intervention required |
| Cost | Higher due to medications | Lower, natural process |
| Breeding Season | Extended or manipulated | Restricted to natural breeding season |
| Offspring Uniformity | High uniformity in lambing dates | Wide variation in lambing times |
Understanding Estrus Synchronization in Sheep
Estrus synchronization in sheep involves manipulating hormonal cycles to induce simultaneous ovulation, enhancing breeding efficiency and lambing management. This technique uses progesterone treatments or prostaglandin injections to control and predict ovulation timing, contrasting with the natural, variable estrus cycle of 16 to 17 days. Understanding estrus synchronization enables precise mating schedules, improving flock productivity and genetic selection outcomes.
Overview of the Natural Breeding Cycle
The natural breeding cycle in sheep is regulated by photoperiod, typically occurring in the fall when decreasing daylight triggers estrus. Ewes exhibit a seasonal, polyestrous pattern with estrus cycles lasting approximately 17 days and a fertile window of 24 to 36 hours. Understanding this timing is crucial for optimizing lambing outcomes without the use of hormonal interventions.
Key Benefits of Estrus Synchronization
Estrus synchronization in sheep enables precise control over breeding timing, increasing lambing uniformity and enhancing flock management efficiency. This technique improves reproductive performance by allowing targeted use of superior rams, reducing the breeding season length and optimizing resource allocation. Key benefits include higher pregnancy rates, streamlined lambing periods, and better alignment with market demands.
Advantages of Natural Breeding Timing
Natural breeding timing in sheep aligns with the flock's inherent reproductive rhythms, promoting higher conception rates and healthier lambs by avoiding stress-related hormonal disruptions. This method reduces labor and hormone treatment costs associated with estrus synchronization, ensuring more sustainable and welfare-friendly flock management. Additionally, natural cycles support genetic diversity by allowing selective mating over extended periods instead of fixed breeding windows.
Hormonal Methods for Estrus Control
Hormonal methods for estrus synchronization in sheep utilize prostaglandins, progesterone, and gonadotropins to precisely control and predict ovulation timing, enhancing breeding efficiency compared to the natural cycle's variability. These protocols synchronize multiple ewes' estrus, optimizing artificial insemination and flock management by reducing breeding season length and improving lambing rates. Controlled hormonal interventions help producers achieve more uniform lambing intervals, ensure better resource allocation, and increase genetic improvement opportunities in sheep breeding programs.
Impact on Lambing Predictability
Estrus synchronization in sheep breeding significantly enhances lambing predictability by aligning the reproductive cycles of ewes, allowing for a concentrated and manageable lambing period. In contrast, the natural cycle results in more staggered lambing, complicating labor and resource planning for shepherds. The controlled timing achieved through synchronization improves flock management efficiency and optimizes nutritional and veterinary interventions during lambing.
Health and Welfare Considerations
Estrus synchronization in sheep breeding enables precise control over reproductive timing, reducing the frequency of handling and minimizing stress-related health issues compared to natural cycles. Hormonal treatments used for synchronization must be carefully managed to avoid adverse effects on sheep welfare, including potential disruptions to natural hormonal balance. Natural cycle breeding promotes innate behaviors and physiological rhythms but may increase risks of uneven lambing periods and related health complications due to less predictable timing.
Costs and Labor Requirements
Estrus synchronization in sheep breeding reduces unpredictability by aligning ovulation, resulting in more efficient use of labor and resources compared to natural cycles, which require prolonged monitoring. The costs of synchronization involve hormonal treatments such as prostaglandins or CIDRs, typically ranging from $3 to $10 per ewe, whereas natural cycles eliminate hormonal expenses but increase labor hours for heat detection. Economic analyses highlight that synchronization can enhance flock management and lambing uniformity, offsetting upfront expenses with improved reproductive efficiency and streamlined labor demands.
Success Rates: Synchronization vs Natural Cycle
Estrus synchronization in sheep breeding significantly improves lambing distribution by aligning ovulation, resulting in more concentrated and predictable lambing periods. Success rates of synchronized cycles often exceed 70%, compared to variable success rates in natural cycles, which depend on seasonal and environmental factors. Controlled timing via synchronization allows for optimized resource management and enhanced reproductive efficiency compared to the natural estrous cycle.
Choosing the Best Approach for Your Flock
Estrus synchronization in sheep enables precise control over breeding timelines, increasing lambing uniformity and improving flock management efficiency. Natural cycling relies on the ewe's inherent reproductive rhythms, offering a low-intervention approach but with less predictability in lambing dates. Selecting the optimal method depends on flock size, breeding goals, and resource availability, with synchronization favored for intensive production systems and natural cycling suited for extensive or low-input operations.
Estrus Synchronization vs Natural Cycle for Sheep Breeding Timing Infographic
 petrevi.com
petrevi.com