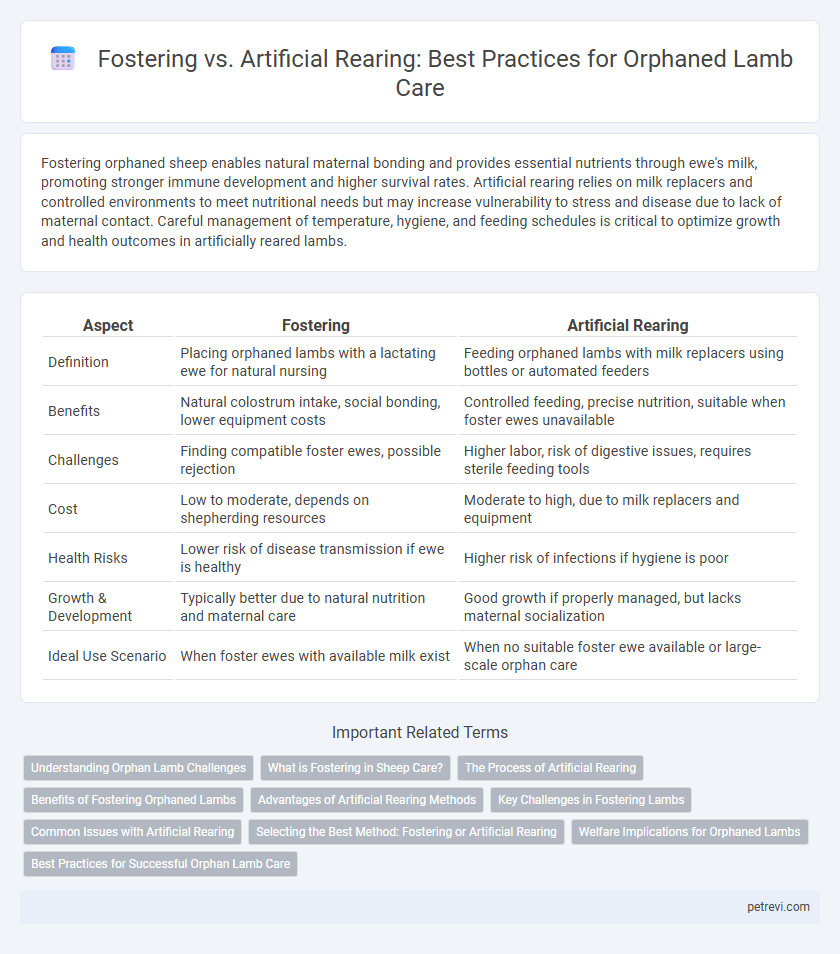
Fostering orphaned sheep enables natural maternal bonding and provides essential nutrients through ewe's milk, promoting stronger immune development and higher survival rates. Artificial rearing relies on milk replacers and controlled environments to meet nutritional needs but may increase vulnerability to stress and disease due to lack of maternal contact. Careful management of temperature, hygiene, and feeding schedules is critical to optimize growth and health outcomes in artificially reared lambs.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Fostering | Artificial Rearing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Placing orphaned lambs with a lactating ewe for natural nursing | Feeding orphaned lambs with milk replacers using bottles or automated feeders |
| Benefits | Natural colostrum intake, social bonding, lower equipment costs | Controlled feeding, precise nutrition, suitable when foster ewes unavailable |
| Challenges | Finding compatible foster ewes, possible rejection | Higher labor, risk of digestive issues, requires sterile feeding tools |
| Cost | Low to moderate, depends on shepherding resources | Moderate to high, due to milk replacers and equipment |
| Health Risks | Lower risk of disease transmission if ewe is healthy | Higher risk of infections if hygiene is poor |
| Growth & Development | Typically better due to natural nutrition and maternal care | Good growth if properly managed, but lacks maternal socialization |
| Ideal Use Scenario | When foster ewes with available milk exist | When no suitable foster ewe available or large-scale orphan care |
Understanding Orphan Lamb Challenges
Orphan lambs face critical challenges such as hypothermia, dehydration, and inadequate colostrum intake, which significantly impact their survival and growth. Fostering enables lambs to receive natural maternal care, including warmth and immunological protection, but requires a compatible ewe and careful management to prevent rejection. Artificial rearing offers controlled nutrition through milk replacers and close monitoring, though it demands intensive labor and may result in weaker immune development compared to maternal rearing.
What is Fostering in Sheep Care?
Fostering in sheep care involves placing an orphaned lamb with a foster ewe who accepts and nurses the lamb as her own, ensuring the lamb receives natural maternal care and nutrition essential for healthy growth. This method leverages the ewe's maternal instincts and milk production, promoting better immunity and social development compared to artificial rearing. Effective fostering requires matching the lamb's age with the foster ewe's maternal stage and sometimes using techniques like scent masking to encourage acceptance.
The Process of Artificial Rearing
Artificial rearing of orphaned sheep involves feeding lambs with milk replacers using bottles or automated feeders to ensure proper nutrition and growth. Maintaining strict hygiene and temperature control during the preparation and feeding of milk replacers prevents disease and promotes healthy development. Regular monitoring of lamb weight, health status, and behavioral cues is essential to adjust feeding schedules and ensure optimal welfare.
Benefits of Fostering Orphaned Lambs
Fostering orphaned lambs onto a surrogate ewe ensures natural nutrition through maternal milk, enhancing immune system development and growth rates. This method promotes social bonding and behavioral normalcy, reducing stress and improving long-term welfare compared to artificial rearing. Economic benefits arise from lower labor and feeding costs, while decreasing the risk of digestive disorders common in milk replacer-fed lambs.
Advantages of Artificial Rearing Methods
Artificial rearing methods for sheep orphan care offer precise nutritional control with milk replacers formulated to meet lambs' specific dietary needs, promoting consistent growth and health. This approach minimizes disease transmission risks associated with foster ewes and allows for intensive monitoring of lamb health and development. Additionally, artificial rearing supports lambs abandoned by foster mothers, ensuring survival even when natural maternal care is unavailable.
Key Challenges in Fostering Lambs
Fostering orphan lambs involves key challenges such as maternal acceptance, where ewes may reject lambs due to differing scents or inadequate bonding time. The risk of mismothering and insufficient milk production can lead to undernourished lambs and increased vulnerability to disease. Careful management of ewe-lamb interactions and monitoring of lamb health are critical to improving survival rates in fostering programs.
Common Issues with Artificial Rearing
Common issues with artificial rearing of sheep orphans include inadequate nutrient intake, leading to poor growth rates and weakened immune systems. Challenges such as incorrect milk replacer formulation and improper feeding techniques frequently result in digestive disorders like bloat or diarrhea. Furthermore, artificial rearing limits natural social behaviors, increasing stress and reducing overall welfare.
Selecting the Best Method: Fostering or Artificial Rearing
Selecting the best method for caring for orphaned sheep hinges on factors like resource availability, labor intensity, and lamb health outcomes. Fostering leverages ewes with maternal instincts to nurse lambs naturally, promoting immune system strength and social bonding, whereas artificial rearing demands precise nutrition management using milk replacers and specialized feeding equipment. Research indicates that fostering generally results in higher survival rates and better growth metrics, but artificial rearing offers a controlled alternative when suitable foster ewes are scarce or lambs require intensive care.
Welfare Implications for Orphaned Lambs
Fostering orphaned lambs by placing them with surrogate ewes promotes natural behaviors and improves social bonding, which significantly enhances welfare outcomes compared to artificial rearing. Artificial rearing methods, involving bottle or bucket feeding, may lead to nutritional deficits and increased stress, impacting immune development and growth rates negatively. Prioritizing fostering as a care strategy aligns better with the lambs' physiological and psychological needs, reducing morbidity and mortality rates in orphaned populations.
Best Practices for Successful Orphan Lamb Care
Fostering orphan lambs onto a ewe with a lamb of similar age is the most natural and effective method, ensuring proper nutrition and social bonding crucial for healthy growth. When fostering is not possible, artificial rearing with specially formulated lamb milk replacers and consistent temperature control supports optimal development and immunity in orphan lambs. Maintaining hygiene, monitoring lamb weight daily, and providing a stress-free environment are essential best practices to enhance survival rates and welfare during orphan care.
Fostering vs Artificial Rearing for Sheep Orphan Care Infographic
 petrevi.com
petrevi.com