Lamb milk provides optimal nutrients and antibodies essential for orphaned sheep's healthy growth, closely mimicking natural ewe's milk composition. Replacer milk offers a convenient alternative when lamb milk is unavailable, formulated to support weight gain and immune function but may lack some bioactive compounds. Careful selection between lamb milk and replacer milk impacts the survival rate and development of orphaned lambs.
Table of Comparison
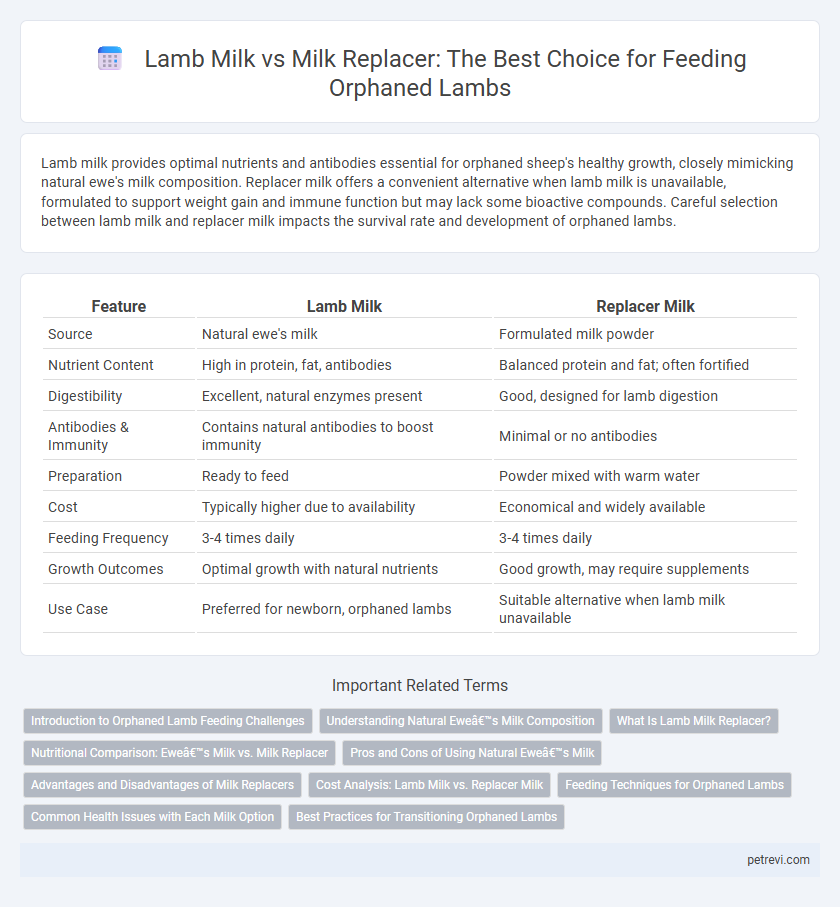
| Feature | Lamb Milk | Replacer Milk |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Natural ewe's milk | Formulated milk powder |
| Nutrient Content | High in protein, fat, antibodies | Balanced protein and fat; often fortified |
| Digestibility | Excellent, natural enzymes present | Good, designed for lamb digestion |
| Antibodies & Immunity | Contains natural antibodies to boost immunity | Minimal or no antibodies |
| Preparation | Ready to feed | Powder mixed with warm water |
| Cost | Typically higher due to availability | Economical and widely available |
| Feeding Frequency | 3-4 times daily | 3-4 times daily |
| Growth Outcomes | Optimal growth with natural nutrients | Good growth, may require supplements |
| Use Case | Preferred for newborn, orphaned lambs | Suitable alternative when lamb milk unavailable |
Introduction to Orphaned Lamb Feeding Challenges
Orphaned lambs face critical growth and health challenges due to the lack of natural ewe milk intake. Lamb milk, rich in essential nutrients, antibodies, and bioactive compounds, closely mimics the composition of maternal milk, supporting immune function and development. Replacer milk formulas vary in quality and nutrient balance, making the choice crucial for preventing malnutrition and promoting optimal lamb survival rates.
Understanding Natural Ewe’s Milk Composition
Natural ewe's milk contains approximately 5-7% fat, 5-6% protein, and 4-5% lactose, providing essential nutrients crucial for lamb growth and immune support. The high levels of casein and specific fatty acids in ewe's milk promote proper digestive development and energy supply in orphaned lambs. Replacer milk must closely match these compositional elements to ensure optimal health, weight gain, and survival rates in lambs deprived of their mother's milk.
What Is Lamb Milk Replacer?
Lamb milk replacer is a specially formulated, powder-based feed designed to mimic the nutritional profile of natural ewe's milk, providing essential proteins, fats, vitamins, and minerals necessary for the healthy growth of orphaned or rejected lambs. It offers a practical alternative when maternal milk is unavailable, promoting optimal weight gain and immune development. Proper preparation and temperature control of lamb milk replacer ensure maximum digestibility and nutrient absorption critical for lamb survival.
Nutritional Comparison: Ewe’s Milk vs. Milk Replacer
Ewe's milk provides optimal nutrition for orphaned lambs, containing high levels of fat (about 6-7%) and protein (5-6%), essential for growth and immune development. Milk replacers vary in composition but typically lack the bioactive compounds and tailored nutrient balance found in ewe's milk, often containing lower fat and protein concentrations. Selecting a milk replacer fortified with vitamins, minerals, and proper energy content can help approximate the nutritional benefits of natural ewe's milk.
Pros and Cons of Using Natural Ewe’s Milk
Natural ewe's milk provides essential nutrients and antibodies, promoting strong immune system development in orphaned lambs and enhancing overall growth performance. However, its availability is limited, and the risk of disease transmission or inconsistencies in milk quality can pose significant challenges. Despite these drawbacks, ewe's milk remains the optimal choice for lamb feeding due to its high digestibility and compatibility with the lamb's digestive system.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Milk Replacers
Milk replacers for orphaned lambs provide consistent nutrition tailored to promote rapid growth and are less susceptible to contamination compared to natural ewe's milk. These formulations often contain essential vitamins, minerals, and proteins, but may lack some bioactive components and antibodies found in maternal milk, potentially affecting immune development. The ease of storage and longer shelf life of milk replacers offer convenience, though cost and possible digestive issues require careful management during lamb rearing.
Cost Analysis: Lamb Milk vs. Replacer Milk
Lamb milk sourced directly from ewes provides higher nutritional value at a lower cost compared to commercial replacer milk, which often includes added vitamins and minerals but comes with increased expenses. Replacer milk formulas can range from $1.50 to $3.00 per feeding, while natural lamb milk feeding costs are mainly limited to labor and equipment, significantly reducing overall expenditure. Farm operations balancing quality and cost may choose natural lamb milk for economic efficiency, reserving replacer milk for emergency use or when ewes are unavailable.
Feeding Techniques for Orphaned Lambs
Lamb milk from the ewe provides essential nutrients and antibodies crucial for the development of orphaned lambs, making it the preferred option when available. Replacer milk formulas are carefully designed to mimic ewe milk's composition, offering a practical alternative when natural lamb milk is not an option, ensuring proper growth and immune support. Feeding techniques for orphaned lambs emphasize frequent, small feedings using bottle or tube feeding methods to prevent digestive issues and promote optimal nutrient absorption.
Common Health Issues with Each Milk Option
Lamb milk provides essential nutrients and antibodies that support the natural immune system development in orphaned sheep, reducing the risk of digestive issues and scours commonly seen with replacer milk. Replacer milk, while convenient, often lacks specific bioactive compounds found in ewe's milk, leading to higher incidences of diarrhea and poor weight gain. Careful formulation of replacer milk and gradual feeding transitions are crucial to minimize gastrointestinal disturbances and ensure optimal growth in orphaned lambs.
Best Practices for Transitioning Orphaned Lambs
When transitioning orphaned lambs from ewe's milk to milk replacer, gradual introduction over 7 to 10 days is essential to minimize digestive upset and ensure optimal nutrient absorption. Select a milk replacer formulated specifically for lambs, with balanced protein, fat, and vitamins closely matching ewe milk composition to promote healthy growth and immune function. Regularly monitor lambs for signs of feeding tolerance and adjust feeding frequency and volume based on individual appetite and weight gain.
Lamb Milk vs Replacer Milk for Orphaned Sheep Feeding Infographic
 petrevi.com
petrevi.com