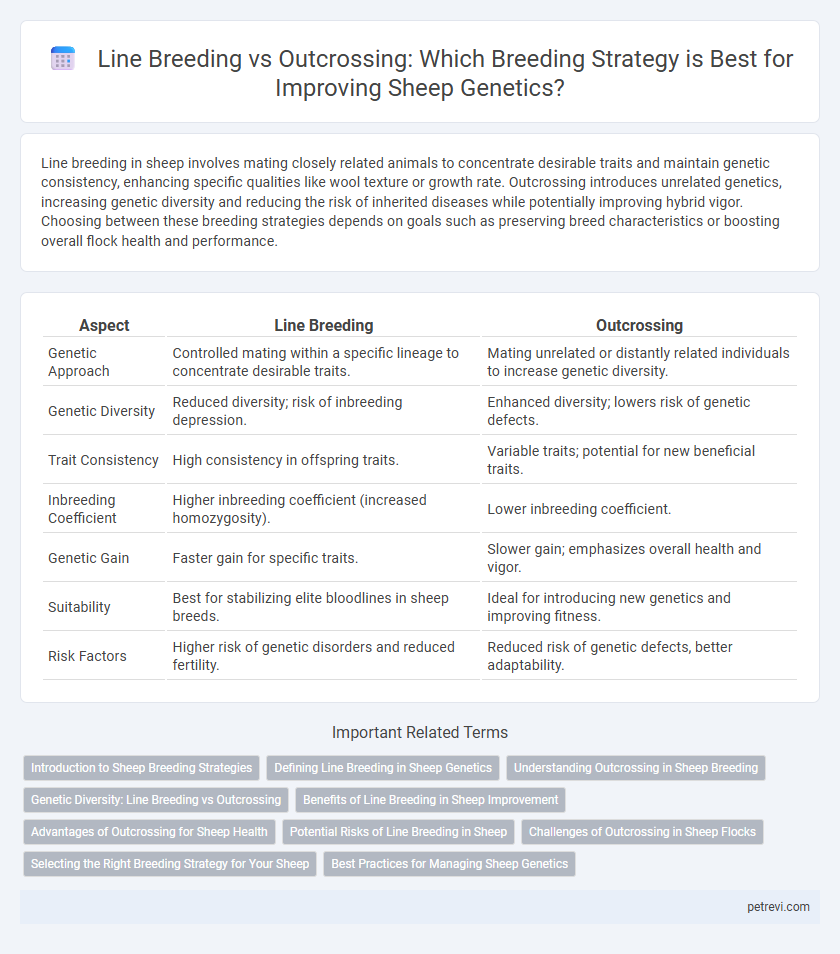
Line breeding in sheep involves mating closely related animals to concentrate desirable traits and maintain genetic consistency, enhancing specific qualities like wool texture or growth rate. Outcrossing introduces unrelated genetics, increasing genetic diversity and reducing the risk of inherited diseases while potentially improving hybrid vigor. Choosing between these breeding strategies depends on goals such as preserving breed characteristics or boosting overall flock health and performance.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Line Breeding | Outcrossing |
|---|---|---|
| Genetic Approach | Controlled mating within a specific lineage to concentrate desirable traits. | Mating unrelated or distantly related individuals to increase genetic diversity. |
| Genetic Diversity | Reduced diversity; risk of inbreeding depression. | Enhanced diversity; lowers risk of genetic defects. |
| Trait Consistency | High consistency in offspring traits. | Variable traits; potential for new beneficial traits. |
| Inbreeding Coefficient | Higher inbreeding coefficient (increased homozygosity). | Lower inbreeding coefficient. |
| Genetic Gain | Faster gain for specific traits. | Slower gain; emphasizes overall health and vigor. |
| Suitability | Best for stabilizing elite bloodlines in sheep breeds. | Ideal for introducing new genetics and improving fitness. |
| Risk Factors | Higher risk of genetic disorders and reduced fertility. | Reduced risk of genetic defects, better adaptability. |
Introduction to Sheep Breeding Strategies
Line breeding in sheep focuses on mating animals with common ancestors to concentrate desirable genetic traits and enhance uniformity within the flock. Outcrossing involves breeding unrelated sheep to introduce new genetic diversity, improving overall flock health and reducing the risk of inherited defects. Both strategies are essential for managing genetic progress and maintaining a resilient and productive sheep population.
Defining Line Breeding in Sheep Genetics
Line breeding in sheep genetics involves mating closely related individuals within a specific bloodline to reinforce desirable traits and maintain genetic consistency. This strategy helps preserve superior characteristics by concentrating genes from a particular ancestor while minimizing the risks associated with inbreeding. Effective line breeding programs require careful selection and monitoring to enhance flock performance and sustain valuable genetic qualities over generations.
Understanding Outcrossing in Sheep Breeding
Outcrossing in sheep breeding involves mating individuals from different genetic lines to enhance genetic diversity and reduce the risk of hereditary diseases. This approach can improve overall flock health, vigor, and adaptability by introducing new traits and preventing inbreeding depression common in line breeding. Outcrossing strategies are essential for maintaining strong, resilient sheep populations with balanced genetics.
Genetic Diversity: Line Breeding vs Outcrossing
Line breeding in sheep enhances specific desirable traits by mating related individuals, but it can reduce genetic diversity and increase the risk of hereditary disorders. Outcrossing introduces unrelated genetic material, boosting genetic diversity and improving overall flock health and adaptability. Maintaining a balance between line breeding and outcrossing ensures optimized genetic traits while preserving genetic variation essential for long-term flock resilience.
Benefits of Line Breeding in Sheep Improvement
Line breeding in sheep enhances genetic consistency by concentrating desirable traits within the flock, leading to improved uniformity in wool quality, growth rates, and disease resistance. This method helps preserve superior bloodlines while minimizing genetic defects, as carefully managed pedigrees maintain a balance between inbreeding and genetic diversity. Consistent application of line breeding accelerates the development of high-performing sheep breeds tailored to specific production goals, maximizing overall flock productivity and profitability.
Advantages of Outcrossing for Sheep Health
Outcrossing in sheep genetics introduces greater genetic diversity, reducing the risk of inherited diseases and improving overall flock health. Enhanced heterozygosity from outcrossing contributes to stronger immune systems and increased resistance to parasites and environmental stressors. This approach supports sustainable breeding practices by maintaining adaptability and vitality within sheep populations.
Potential Risks of Line Breeding in Sheep
Line breeding in sheep concentrates genetic traits by mating closely related individuals, increasing the risk of recessive genetic disorders and reduced genetic diversity. This practice can lead to inbreeding depression, manifesting as reduced fertility, slower growth rates, and heightened susceptibility to diseases. Maintaining a careful balance is crucial to avoid accumulating harmful alleles that compromise flock health and productivity.
Challenges of Outcrossing in Sheep Flocks
Outcrossing in sheep flocks introduces significant challenges, including increased risk of disease transmission and the dilution of desirable genetic traits, which can complicate breeding goals. Managing genetic diversity while maintaining flock uniformity requires meticulous record-keeping and careful selection to avoid unintended genetic incompatibilities. The unpredictable nature of outcrossing can lead to variability in offspring performance, impacting traits like wool quality and growth rates essential for commercial sheep production.
Selecting the Right Breeding Strategy for Your Sheep
Line breeding focuses on reinforcing desirable traits within a sheep flock by mating related individuals, which helps maintain genetic consistency and improves specific qualities like wool texture and growth rates. Outcrossing introduces genetic diversity by breeding unrelated sheep, reducing inbreeding depression risks and enhancing traits such as disease resistance and overall flock vitality. Choosing the appropriate breeding strategy depends on your flock's genetic goals, health status, and the need to balance trait improvement with genetic diversity.
Best Practices for Managing Sheep Genetics
Line breeding in sheep genetics enhances desirable traits by mating closely related individuals, preserving genetic consistency and improving flock uniformity. Outcrossing introduces new genetic material from unrelated sheep, increasing genetic diversity and reducing the risk of inherited diseases. Best practices involve balancing line breeding to maintain trait quality while periodically outcrossing to prevent inbreeding depression and promote flock health.
Line Breeding vs Outcrossing for Sheep Genetics Infographic
 petrevi.com
petrevi.com