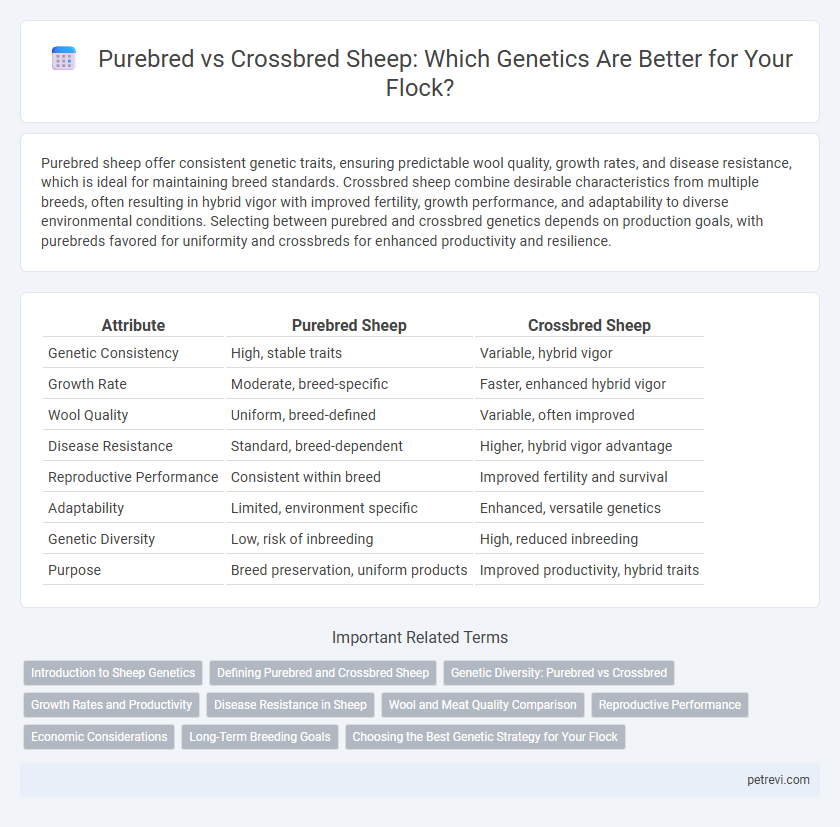
Purebred sheep offer consistent genetic traits, ensuring predictable wool quality, growth rates, and disease resistance, which is ideal for maintaining breed standards. Crossbred sheep combine desirable characteristics from multiple breeds, often resulting in hybrid vigor with improved fertility, growth performance, and adaptability to diverse environmental conditions. Selecting between purebred and crossbred genetics depends on production goals, with purebreds favored for uniformity and crossbreds for enhanced productivity and resilience.
Table of Comparison
| Attribute | Purebred Sheep | Crossbred Sheep |
|---|---|---|
| Genetic Consistency | High, stable traits | Variable, hybrid vigor |
| Growth Rate | Moderate, breed-specific | Faster, enhanced hybrid vigor |
| Wool Quality | Uniform, breed-defined | Variable, often improved |
| Disease Resistance | Standard, breed-dependent | Higher, hybrid vigor advantage |
| Reproductive Performance | Consistent within breed | Improved fertility and survival |
| Adaptability | Limited, environment specific | Enhanced, versatile genetics |
| Genetic Diversity | Low, risk of inbreeding | High, reduced inbreeding |
| Purpose | Breed preservation, uniform products | Improved productivity, hybrid traits |
Introduction to Sheep Genetics
Purebred sheep offer consistent genetic traits, enabling predictable outcomes in wool quality, growth rates, and disease resistance. Crossbred sheep combine diverse genetic material to enhance hybrid vigor, resulting in improved fertility, survival rates, and adaptability to varied environments. Understanding sheep genetics requires analyzing how purebred reliability contrasts with crossbred heterosis to optimize breeding strategies.
Defining Purebred and Crossbred Sheep
Purebred sheep possess a well-documented lineage tracing back to a single breed, ensuring consistent genetic traits such as wool quality, meat yield, and disease resistance. Crossbred sheep result from mating two or more distinct breeds, combining diverse genetic traits to enhance growth rates, fertility, and adaptability to varying environmental conditions. Understanding the genetics of purebred versus crossbred sheep is essential for selective breeding programs aimed at optimizing production efficiency and animal health.
Genetic Diversity: Purebred vs Crossbred
Crossbred sheep typically exhibit greater genetic diversity compared to purebred sheep, which enhances their adaptability and resilience to diseases. Purebred sheep maintain consistent traits but may suffer from inbreeding depression, leading to reduced fertility and increased susceptibility to genetic disorders. Incorporating crossbreeding strategies can optimize genetic traits while preserving overall herd health and performance.
Growth Rates and Productivity
Purebred sheep exhibit consistent growth rates and predictable productivity due to their uniform genetics, making them ideal for maintaining breed standards. Crossbred sheep often demonstrate hybrid vigor, resulting in faster growth rates and enhanced productivity through improved feed conversion and disease resistance. Selecting between purebred and crossbred genetics depends on specific production goals, such as maximizing lambing rates or optimizing carcass quality.
Disease Resistance in Sheep
Purebred sheep often carry specific genetic traits linked to breed standards but can be more susceptible to certain diseases due to limited genetic diversity. Crossbred sheep benefit from hybrid vigor, enhancing disease resistance by combining diverse genetic material and reducing the prevalence of inherited disorders. Utilizing crossbreeding strategies can improve overall flock health and resilience against parasites, infections, and environmental stressors.
Wool and Meat Quality Comparison
Purebred sheep offer consistent wool quality with specific fiber fineness and staple length, optimizing textile applications, while crossbred sheep often exhibit hybrid vigor, enhancing meat yield and growth rates due to genetic diversity. Wool from purebred breeds like Merino is highly prized for softness and uniformity, whereas crossbreds may produce coarser but more durable fleece suitable for diverse products. Meat quality in crossbred sheep benefits from improved carcass traits and flavor profiles, balancing the lean muscle development of purebreds with the robustness of local breeds.
Reproductive Performance
Purebred sheep often exhibit consistent reproductive traits due to genetically uniform lineage, which can simplify breeding management and predictability of lambing rates. Crossbred sheep benefit from heterosis or hybrid vigor, showing improved fertility, higher lamb survival rates, and increased prolificacy compared to purebreds. Reproductive performance in crossbreds typically surpasses purebreds, making them advantageous for maximizing flock productivity.
Economic Considerations
Purebred sheep generally command higher market prices due to predictable traits and established breed reputations, making them valuable for specialized wool and meat production. Crossbred sheep offer enhanced hybrid vigor, often resulting in improved growth rates, fertility, and disease resistance, which can lower production costs and increase overall profitability. Economic decisions hinge on market demands and production goals, where purebreds suit niche markets and crossbreds maximize efficiency in commercial operations.
Long-Term Breeding Goals
Purebred sheep maintain genetic consistency, which supports predictable traits essential for achieving specific long-term breeding goals such as fiber quality and disease resistance. Crossbred sheep introduce heterosis, enhancing traits like growth rate and fertility, which can accelerate improvements in flock performance over generations. Strategic integration of purebred lines with crossbreeding programs optimizes genetic diversity, balancing trait stability and overall productivity for sustainable sheep breeding.
Choosing the Best Genetic Strategy for Your Flock
Purebred sheep offer consistent traits and predictable genetic outcomes, making them ideal for producers targeting specific breed characteristics and uniformity in wool or meat quality. Crossbred sheep benefit from hybrid vigor, often exhibiting improved growth rates, fertility, and disease resistance, which can enhance overall flock performance. Selecting the best genetic strategy depends on production goals, whether prioritizing breed purity or maximizing productivity through genetic diversity.
Purebred vs Crossbred for Sheep Genetics Infographic
 petrevi.com
petrevi.com