Sheep wool provides superior insulation and moisture-wicking properties compared to hair, making it ideal for colder climates and textile production. Hair sheep have coats that shed naturally and require less maintenance, offering advantages in hot or humid environments where wool might cause overheating or matting. Understanding the differences between wool and hair sheep helps optimize livestock management and product use based on environmental conditions and market demand.
Table of Comparison
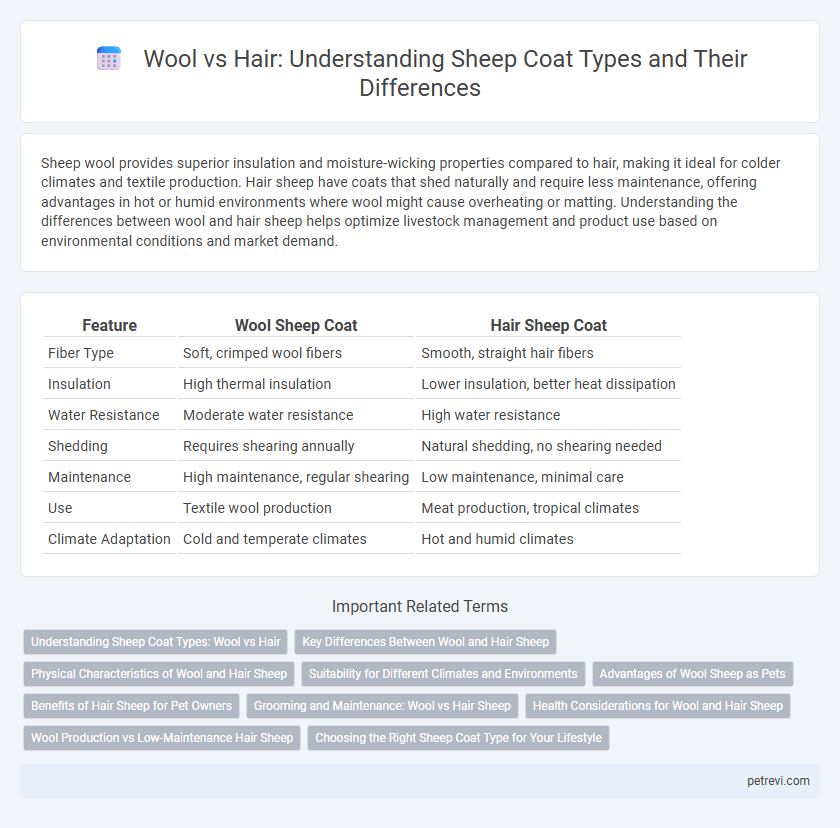
| Feature | Wool Sheep Coat | Hair Sheep Coat |
|---|---|---|
| Fiber Type | Soft, crimped wool fibers | Smooth, straight hair fibers |
| Insulation | High thermal insulation | Lower insulation, better heat dissipation |
| Water Resistance | Moderate water resistance | High water resistance |
| Shedding | Requires shearing annually | Natural shedding, no shearing needed |
| Maintenance | High maintenance, regular shearing | Low maintenance, minimal care |
| Use | Textile wool production | Meat production, tropical climates |
| Climate Adaptation | Cold and temperate climates | Hot and humid climates |
Understanding Sheep Coat Types: Wool vs Hair
Sheep coat types are primarily categorized into wool and hair, each serving different purposes and adapting to various climates. Wool coats provide insulation and moisture-wicking properties, making them ideal for colder environments, while hair coats offer better heat tolerance and are more common in tropical or arid regions. Understanding these coat types is essential for selecting sheep breeds suited to specific agricultural practices and environmental conditions.
Key Differences Between Wool and Hair Sheep
Wool sheep have fleece composed primarily of fine, crimped wool fibers that provide excellent insulation and are highly valued for textile production. Hair sheep, in contrast, possess coats made of coarse, straight hair fibers that shed naturally and require less maintenance, making them well-suited for warmer climates. Key differences include fiber texture, insulation properties, and adaptability, influencing their agricultural uses and economic value.
Physical Characteristics of Wool and Hair Sheep
Sheep with wool coats have dense, curly fibers that provide excellent insulation and water resistance, making them well-suited for colder climates. Hair sheep feature straight, smooth hairs that shed seasonally and require less maintenance, offering better heat tolerance in warmer environments. Wool fibers tend to be finer and more elastic, whereas hair fibers are coarser and less crimped, impacting texture and durability.
Suitability for Different Climates and Environments
Sheep wool, known for its dense, insulating properties, offers superior warmth and moisture-wicking abilities, making it ideal for cold and damp climates. Hair sheep possess a lighter, more breathable coat that adapts well to hot, arid environments by providing better heat dissipation and resistance to parasites. Selecting wool or hair sheep breeds depends largely on regional climate conditions and the specific requirements for fiber production or environmental resilience.
Advantages of Wool Sheep as Pets
Wool sheep offer significant advantages as pets due to their soft, insulating fleece that provides warmth and comfort in various climates. Their wool can be regularly sheared, allowing for grooming that helps maintain cleanliness and reduces pests. Additionally, wool sheep are often valued for their gentle temperament and adaptability, making them well-suited for companionship and small-scale farming environments.
Benefits of Hair Sheep for Pet Owners
Hair sheep offer benefits for pet owners by requiring less maintenance compared to wool sheep, as their hair naturally sheds and does not need shearing. This natural shedding reduces the risk of matting and skin infections, promoting better hygiene and comfort for the sheep. Hair sheep are also well-suited to warmer climates due to their lighter coats, making them easier to manage year-round.
Grooming and Maintenance: Wool vs Hair Sheep
Wool sheep require regular shearing at least once a year to prevent matting and maintain fleece quality, making grooming more labor-intensive compared to hair sheep. Hair sheep naturally shed their coats, reducing the need for shearing and extensive grooming, which lowers maintenance time and costs. The high lanolin content in wool necessitates additional cleaning to manage dirt and parasites, whereas hair sheep typically have fewer issues with skin irritations and are easier to care for in varied climates.
Health Considerations for Wool and Hair Sheep
Wool sheep possess a dense, insulating fleece that provides excellent protection against cold weather but requires regular shearing to prevent overheating and parasite infestations. Hair sheep naturally shed their coats, reducing the risk of wool-related skin diseases and minimizing the need for grooming, which can improve overall health maintenance. Both coat types influence thermal regulation and disease susceptibility, necessitating tailored health management practices for optimal sheep wellbeing.
Wool Production vs Low-Maintenance Hair Sheep
Wool sheep produce dense, crimped fiber ideal for textile manufacturing, contributing significantly to the global wool industry with breeds like Merino leading in yield and quality. Hair sheep have a coat of smooth, hair-like fibers requiring less shearing and maintenance, making them suitable for low-input farming systems and warmer climates. Choosing between wool and hair sheep impacts wool production volume, maintenance needs, and adaptation to environmental conditions.
Choosing the Right Sheep Coat Type for Your Lifestyle
Sheep with wool coats provide excellent insulation and are ideal for colder climates, offering warmth and flexibility for textile production. Hair sheep, with their low-maintenance coats, shed naturally and are well-suited for warmer environments or owners seeking minimal grooming. Selecting the right sheep coat type depends on climate, intended use, and desired upkeep level to match your lifestyle efficiently.
Wool vs Hair for Sheep Coat Type Infographic
 petrevi.com
petrevi.com