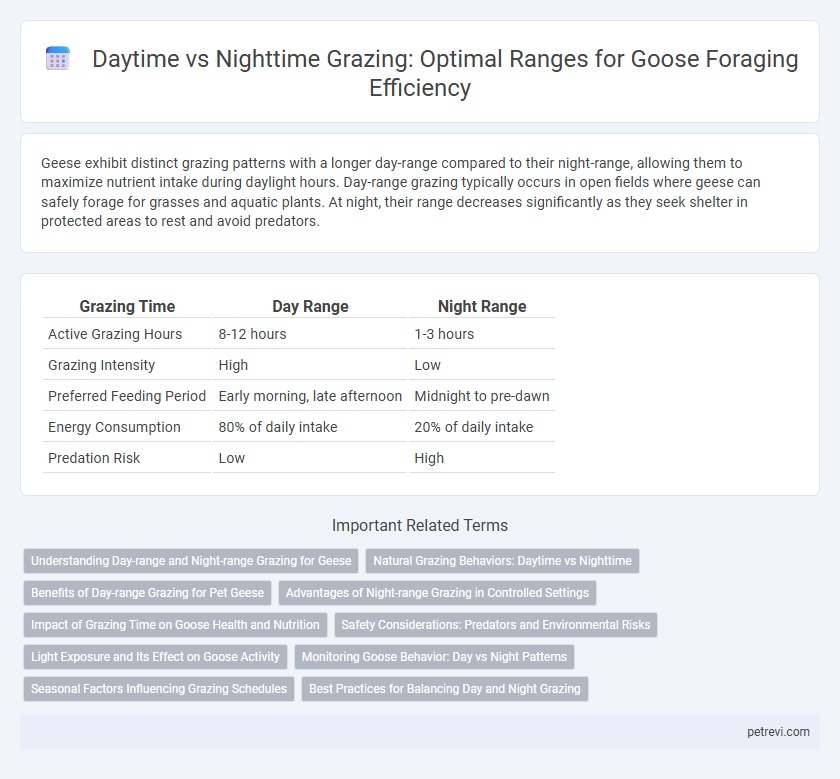
Geese exhibit distinct grazing patterns with a longer day-range compared to their night-range, allowing them to maximize nutrient intake during daylight hours. Day-range grazing typically occurs in open fields where geese can safely forage for grasses and aquatic plants. At night, their range decreases significantly as they seek shelter in protected areas to rest and avoid predators.
Table of Comparison
| Grazing Time | Day Range | Night Range |
|---|---|---|
| Active Grazing Hours | 8-12 hours | 1-3 hours |
| Grazing Intensity | High | Low |
| Preferred Feeding Period | Early morning, late afternoon | Midnight to pre-dawn |
| Energy Consumption | 80% of daily intake | 20% of daily intake |
| Predation Risk | Low | High |
Understanding Day-range and Night-range Grazing for Geese
Geese exhibit distinct grazing patterns during day-range and night-range periods, with day-range grazing typically involving more active foraging in open fields and night-range grazing occurring in safer, sheltered areas to avoid predators. Understanding these grazing behaviors requires analyzing habitat preference, feeding efficiency, and predator avoidance strategies, which influence their energy intake and overall health. Monitoring geese during these times helps optimize conservation efforts and land management practices for maintaining balanced ecosystems.
Natural Grazing Behaviors: Daytime vs Nighttime
Goose grazing time varies significantly between day-range and night-range due to natural feeding behaviors, with most foraging occurring during daylight hours when visibility aids in locating food. Nighttime grazing is minimal as geese rely on daylight to efficiently graze on grasses and aquatic plants, conserving energy and avoiding predators. Studies show that geese extend their grazing period into dusk and dawn but reduce activity during complete darkness, optimizing nutrient intake while maintaining safety.
Benefits of Day-range Grazing for Pet Geese
Day-range grazing offers pet geese increased access to natural forage, promoting higher nutrient intake and improved digestion compared to night-range grazing. Exposure to sunlight during daytime grazing enhances vitamin D synthesis, supporting stronger bone development and overall health. Furthermore, day-range grazing reduces the risk of nocturnal predation, providing a safer environment for pet geese to thrive.
Advantages of Night-range Grazing in Controlled Settings
Night-range grazing for geese in controlled settings enhances feed efficiency by reducing daytime heat stress and maximizing forage intake during cooler hours. This approach promotes better digestion and nutrient absorption due to extended rumination periods at night. Controlled night-range environments also limit predator exposure and human disturbances, leading to improved welfare and consistent grazing behavior.
Impact of Grazing Time on Goose Health and Nutrition
Goose grazing time significantly influences their health and nutrition by aligning with their natural foraging behaviors during day and night ranges. Day-range grazing typically provides geese with access to higher-quality forage rich in nutrients, essential for energy and growth, whereas night-range grazing often involves lower-quality forage, potentially limiting nutritional intake. Optimizing grazing schedules to maximize daytime foraging can enhance digestive efficiency, improve nutrient absorption, and support overall goose health and vitality.
Safety Considerations: Predators and Environmental Risks
Goose grazing time varies significantly between day and night due to safety considerations involving predators and environmental risks. Day-range grazing allows geese to benefit from better visibility, reducing vulnerability to predators such as foxes and hawks, while night-range grazing increases exposure to nocturnal predators like owls and raccoons. Environmental risks including low temperatures and reduced oxygen levels at night further influence geese to prefer daytime foraging for optimal energy intake and safety.
Light Exposure and Its Effect on Goose Activity
Goose grazing time varies significantly between day-range and night-range due to differences in light exposure, which directly influences their activity patterns. During daylight hours, geese exhibit increased foraging behavior driven by higher visibility and safety, enhancing feeding efficiency and energy intake. Conversely, reduced light levels at night suppress grazing activity, causing geese to rely more on resting or vigilance behaviors to conserve energy and avoid predators.
Monitoring Goose Behavior: Day vs Night Patterns
Goose grazing time varies significantly between day and night, with average day-range activity extending up to 4 hours, while night-range grazing is typically limited to 1-2 hours due to reduced visibility and increased predation risk. Monitoring goose behavior reveals that diurnal foraging peaks during early morning and late afternoon when food availability is highest, contrasting with sporadic and cautious night-time grazing. Understanding these patterns aids in habitat management and predicting goose impact on agricultural fields based on light conditions and predator presence.
Seasonal Factors Influencing Grazing Schedules
Goose grazing time varies significantly between day-range and night-range due to seasonal changes in daylight and temperature. During longer daylight hours in spring and summer, geese extend their grazing periods into the night, benefiting from cooler temperatures and increased food availability. In contrast, shorter daylight in autumn and winter limits grazing to daytime hours, as colder nights reduce forage accessibility and increase energy conservation needs.
Best Practices for Balancing Day and Night Grazing
Goose grazing time varies significantly between day-range and night-range, with geese typically grazing for 6 to 8 hours during daylight and 2 to 4 hours at night. Best practices for balancing day and night grazing include providing well-lit, secure pastures to encourage safe nighttime feeding while ensuring adequate forage availability during the day to optimize nutrient intake and prevent overgrazing. Monitoring grass regrowth and goose behavior helps maintain pasture health and promotes sustainable grazing patterns.
Day-range vs Night-range for Goose Grazing Time Infographic
 petrevi.com
petrevi.com