Sheep primarily graze on grasses and herbaceous plants, which provide essential nutrients for their growth and wool production. Browsing, involving the consumption of leaves, twigs, and shrubs, supplements their diet especially when pasture quality declines. Balancing grazing and browsing improves overall nutrition, supporting healthier sheep and more sustainable pasture management.
Table of Comparison
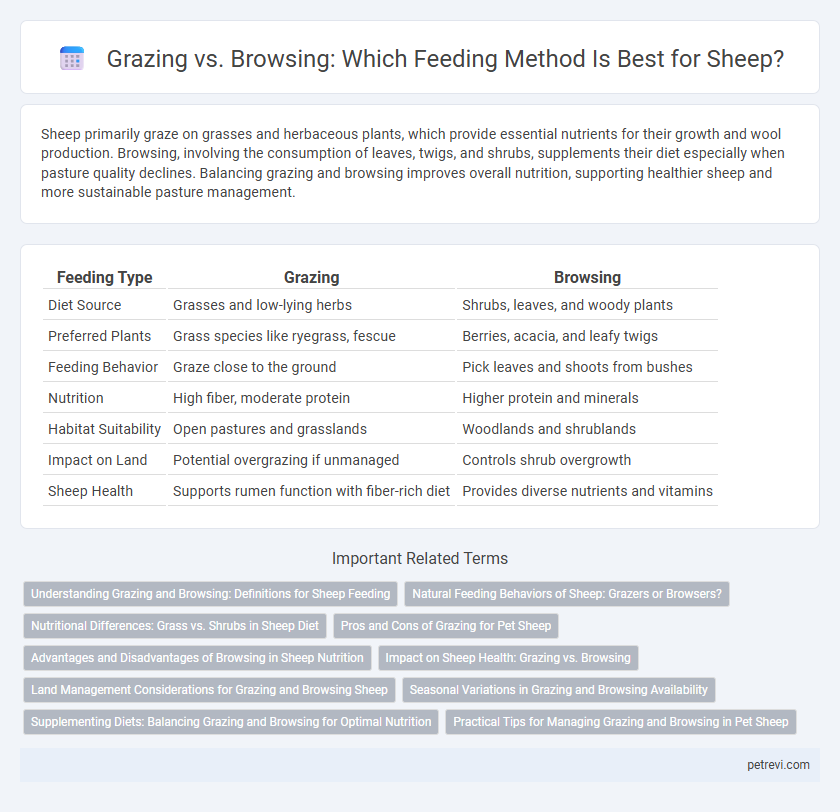
| Feeding Type | Grazing | Browsing |
|---|---|---|
| Diet Source | Grasses and low-lying herbs | Shrubs, leaves, and woody plants |
| Preferred Plants | Grass species like ryegrass, fescue | Berries, acacia, and leafy twigs |
| Feeding Behavior | Graze close to the ground | Pick leaves and shoots from bushes |
| Nutrition | High fiber, moderate protein | Higher protein and minerals |
| Habitat Suitability | Open pastures and grasslands | Woodlands and shrublands |
| Impact on Land | Potential overgrazing if unmanaged | Controls shrub overgrowth |
| Sheep Health | Supports rumen function with fiber-rich diet | Provides diverse nutrients and vitamins |
Understanding Grazing and Browsing: Definitions for Sheep Feeding
Grazing for sheep refers to feeding primarily on grass and low-growing herbaceous plants, while browsing involves consuming leaves, twigs, and shrubs. Understanding these definitions is crucial for sheep nutrition management as grazing supports fiber intake and rumen health, whereas browsing provides essential nutrients and variety. Optimizing sheep diets requires balancing grazing and browsing to enhance forage utilization and overall flock performance.
Natural Feeding Behaviors of Sheep: Grazers or Browsers?
Sheep are primarily grazers, naturally feeding on grasses, herbs, and other low-growing vegetation, which aligns with their digestive physiology adapted to digest fibrous plant material efficiently. While they occasionally browse on shrubs or young leaves, this behavior is supplemental rather than a primary feeding strategy, distinguishing them from true browsers like goats. Understanding these natural feeding behaviors is essential for optimizing pasture management and ensuring proper nutrition in sheep farming.
Nutritional Differences: Grass vs. Shrubs in Sheep Diet
Sheep grazing on grass primarily consume high-fiber, carbohydrate-rich forage that supports rumen fermentation and energy production, while browsing on shrubs provides a diet richer in protein, vitamins, and secondary metabolites like tannins that can influence digestion and parasite control. Grass offers abundant cellulose and hemicellulose, essential for volatile fatty acid synthesis, whereas shrub leaves and twigs contain higher concentrations of crude protein and essential micronutrients such as calcium and magnesium. Balancing grazing and browsing enhances overall sheep nutrition by supplying diverse nutrient profiles and promoting optimal rumen function and health.
Pros and Cons of Grazing for Pet Sheep
Grazing offers pet sheep a natural diet rich in grasses, promoting digestive health and reducing feed costs. However, grazing requires ample pasture space and careful management to prevent overgrazing and parasitic infections. Limited nutritional variety from exclusive grazing can lead to deficiencies, necessitating supplemental feeding for balanced health.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Browsing in Sheep Nutrition
Browsing in sheep nutrition offers the advantage of diversified forage intake, providing access to higher protein and micronutrient levels from shrubs and woody plants compared to typical grass grazing. However, browsing can pose disadvantages such as increased risk of ingesting toxic plants and potential digestive issues due to higher fiber content and varying plant secondary compounds. Effective management is essential to balance the nutritional benefits of browsing with the challenges of plant selection and sheep health monitoring.
Impact on Sheep Health: Grazing vs. Browsing
Grazing on nutrient-rich grasses provides sheep with essential proteins, fiber, and minerals that support rumen function and promote overall health. Browsing on shrubs and leaves offers diverse phytochemicals and tannins that can improve parasite resistance but may reduce digestibility if consumed in excess. Balancing grazing and browsing ensures optimal nutrient intake and enhances sheep's immune response, reducing health risks associated with malnutrition or parasite infestations.
Land Management Considerations for Grazing and Browsing Sheep
Grazing sheep primarily consume grasses and require pasturelands that support dense, nutritious turf, promoting soil stability and reducing erosion through continuous plant cover. Browsing sheep feed on shrubs, woody plants, and forbs, which can help manage brush encroachment and improve biodiversity in overgrown or marginal lands. Effective land management balances grazing and browsing to optimize vegetation control, enhance forage availability, and maintain ecosystem health.
Seasonal Variations in Grazing and Browsing Availability
Seasonal variations significantly influence grazing and browsing availability for sheep, with spring and early summer offering abundant grasses and herbaceous plants for optimal grazing. During late summer and autumn, as grass quality declines, sheep increasingly rely on browsing shrubs and woody plants to meet nutritional needs. Winter often limits grazing options due to snow cover, making browsing vital for sustained intake and overall flock health.
Supplementing Diets: Balancing Grazing and Browsing for Optimal Nutrition
Sheep primarily consume grasses through grazing, but incorporating browsing on shrubs and woody plants supplements their diet with essential nutrients like minerals and vitamins often lacking in grass alone. Balancing grazing and browsing ensures optimal nutrition, promoting better growth, reproduction, and overall health. Strategic supplementation with browse can reduce reliance on external feed inputs while enhancing nutrient diversity in sheep diets.
Practical Tips for Managing Grazing and Browsing in Pet Sheep
Effective management of grazing and browsing in pet sheep involves balancing pasture quality with shrub or tree access to meet their nutritional needs. Regularly rotating grazing areas prevents overgrazing while providing diverse forage such as grasses, clover, and woody plants enhances diet variety and welfare. Implementing controlled browsing allows sheep to consume higher-fiber foliage, improving digestion and reducing parasite loads through natural plant compounds.
Grazing vs Browsing for Sheep Feeding Infographic
 petrevi.com
petrevi.com