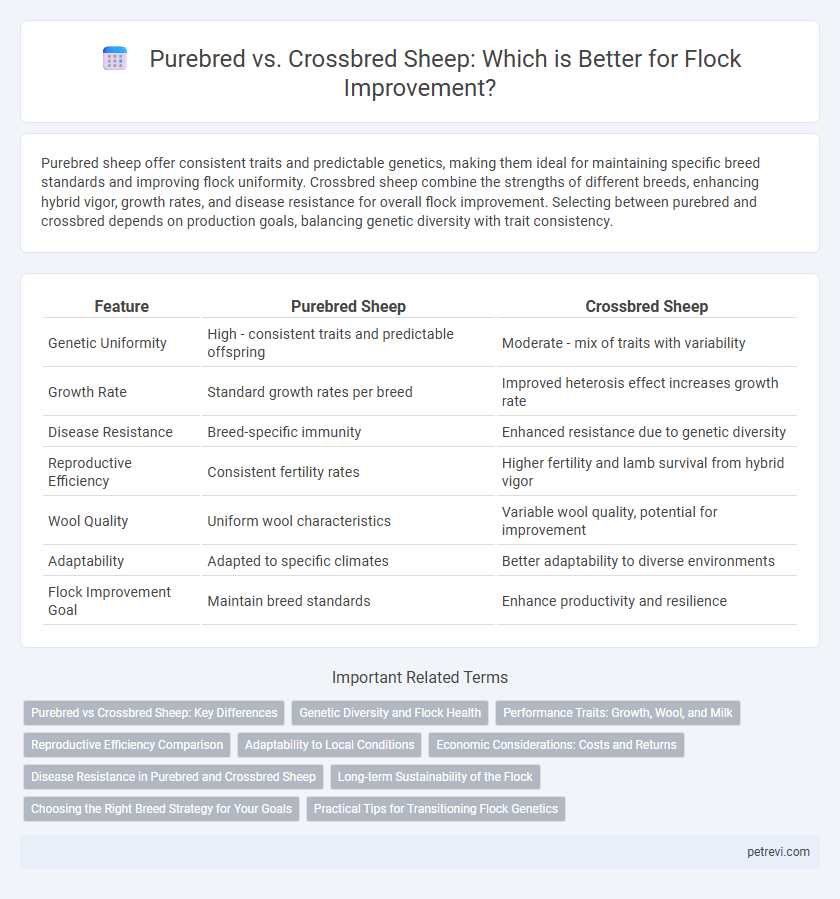
Purebred sheep offer consistent traits and predictable genetics, making them ideal for maintaining specific breed standards and improving flock uniformity. Crossbred sheep combine the strengths of different breeds, enhancing hybrid vigor, growth rates, and disease resistance for overall flock improvement. Selecting between purebred and crossbred depends on production goals, balancing genetic diversity with trait consistency.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Purebred Sheep | Crossbred Sheep |
|---|---|---|
| Genetic Uniformity | High - consistent traits and predictable offspring | Moderate - mix of traits with variability |
| Growth Rate | Standard growth rates per breed | Improved heterosis effect increases growth rate |
| Disease Resistance | Breed-specific immunity | Enhanced resistance due to genetic diversity |
| Reproductive Efficiency | Consistent fertility rates | Higher fertility and lamb survival from hybrid vigor |
| Wool Quality | Uniform wool characteristics | Variable wool quality, potential for improvement |
| Adaptability | Adapted to specific climates | Better adaptability to diverse environments |
| Flock Improvement Goal | Maintain breed standards | Enhance productivity and resilience |
Purebred vs Crossbred Sheep: Key Differences
Purebred sheep come from established breeds with uniform genetic traits, ensuring predictable characteristics such as wool quality, growth rates, and disease resistance. Crossbred sheep result from mating different breeds, combining diverse traits to enhance hybrid vigor, increased fertility, and adaptability to varying environments. Selecting between purebred and crossbred sheep depends on flock goals, whether focusing on breed preservation or improving productivity through genetic diversity.
Genetic Diversity and Flock Health
Purebred sheep offer uniform genetics that maintain specific desirable traits but may reduce genetic diversity, increasing vulnerability to diseases. Crossbred sheep enhance genetic variability, leading to hybrid vigor that improves flock health, resilience, and adaptability. Integrating crossbreeding strategies can strengthen immune responses and reduce susceptibility to common sheep ailments, fostering a robust and sustainable flock.
Performance Traits: Growth, Wool, and Milk
Purebred sheep breeds excel in consistent performance traits such as superior wool quality, defined growth rates, and high milk yield, enabling predictable flock improvement outcomes. Crossbred sheep often demonstrate hybrid vigor, showing enhanced growth rates, improved fertility, and resilience, which can lead to increased overall flock productivity. Strategic use of purebred genetics combined with crossbreeding programs optimizes growth performance, wool fiber characteristics, and milk production for sustainable sheep flock enhancement.
Reproductive Efficiency Comparison
Purebred sheep often exhibit consistent reproductive traits due to uniform genetics, with average lambing rates ranging from 1.2 to 1.5 lambs per ewe annually. Crossbred sheep benefit from heterosis, showing increased fertility, lamb survival, and lambing rates that can exceed 1.6 lambs per ewe per year. Enhanced reproductive efficiency in crossbreds contributes to improved flock productivity and accelerated genetic gain.
Adaptability to Local Conditions
Purebred sheep maintain genetic consistency, ensuring specific traits like wool quality or growth rates, yet they might struggle to adapt swiftly to harsh local environments. Crossbred sheep often exhibit hybrid vigor, combining the strengths of multiple breeds to improve adaptability, disease resistance, and reproductive performance. Selecting crossbred sheep tailored to regional climates enhances flock resilience and productivity under varying local conditions.
Economic Considerations: Costs and Returns
Purebred sheep often involve higher initial costs due to purchase price and specialized breeding management, but they can command premium market prices for uniformity and pedigree. Crossbred sheep typically have lower acquisition and maintenance expenses while benefiting from hybrid vigor, which can enhance growth rates, fertility, and survivability, leading to improved overall flock productivity. Evaluating cost-benefit ratios requires analyzing feed efficiency, lambing rates, and market demand to determine the most profitable strategy for flock improvement based on specific economic goals.
Disease Resistance in Purebred and Crossbred Sheep
Purebred sheep often exhibit strong disease resistance traits specific to their genetic lineage, making them valuable for maintaining flock health in stable environments. Crossbred sheep benefit from hybrid vigor, combining diverse genetic pools to enhance overall immunity and reduce susceptibility to common diseases. Incorporating crossbreeding strategies can improve flock resilience against infections while preserving desirable characteristics from purebred stock.
Long-term Sustainability of the Flock
Purebred sheep offer predictable genetics and consistent traits, supporting breed preservation and market niche specialization. Crossbred sheep enhance genetic diversity, improving disease resistance, fertility, and overall flock robustness for long-term sustainability. Strategic use of both breeding methods balances trait consistency with adaptability, promoting a resilient and productive sheep flock.
Choosing the Right Breed Strategy for Your Goals
Selecting the right breed strategy is crucial for sheep flock improvement, balancing purebred consistency with crossbred hybrid vigor. Purebred sheep provide predictable traits and breed standards essential for specialized production goals, while crossbred sheep offer enhanced growth rates, fertility, and resilience through heterosis. Evaluating production goals, environmental conditions, and market demands guides informed decisions between purebred selection and strategic crossbreeding for optimal flock performance.
Practical Tips for Transitioning Flock Genetics
Selecting purebred sheep ensures consistent traits and predictable performance, ideal for maintaining breed standards in flock improvement. Crossbreeding introduces hybrid vigor, enhancing growth rates, fertility, and disease resistance, which accelerates genetic progress. Gradually integrating crossbred rams while tracking pedigree data enables effective management of genetic diversity without compromising flock uniformity.
Purebred vs Crossbred for Sheep Flock Improvement Infographic
 petrevi.com
petrevi.com